

- HOW TO GET NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 960M DRIVER HOW TO
- HOW TO GET NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 960M DRIVER INSTALL
- HOW TO GET NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 960M DRIVER DRIVERS
- HOW TO GET NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 960M DRIVER DRIVER
- HOW TO GET NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 960M DRIVER FULL
How to set NOMODESET and other kernel boot options in grub2 - both BIOS liveCD & grub first boot ( also UEFI with grub)
HOW TO GET NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 960M DRIVER INSTALL
Many need boot parameters to get into system, or use recovery mode, second line in grub to get to command line to install drivers.Īt grub menu you can use e for edit, scroll to linux line and replace quiet splash with nomodeset.
HOW TO GET NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 960M DRIVER DRIVER
If available driver is new enough for your nVidia card/chip: Ubuntu-drivers devices | grep recommended
HOW TO GET NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 960M DRIVER DRIVERS
# list drivers available, same list as system settings, software updates, additional drivers or last tab If new driver not in repository, you can add the ppa that has all the new drivers.

run file from nVidia as you have to manaully re-update with every kernel update. You must always purge before new driver install.Īnd do not install the. A new driver does not delete the old one. If you attempt to install more than one nVidia driver, you get conflicts. Those with AMD have an issue with newer system not working with current AMD proprietary driver, but nVidia works.

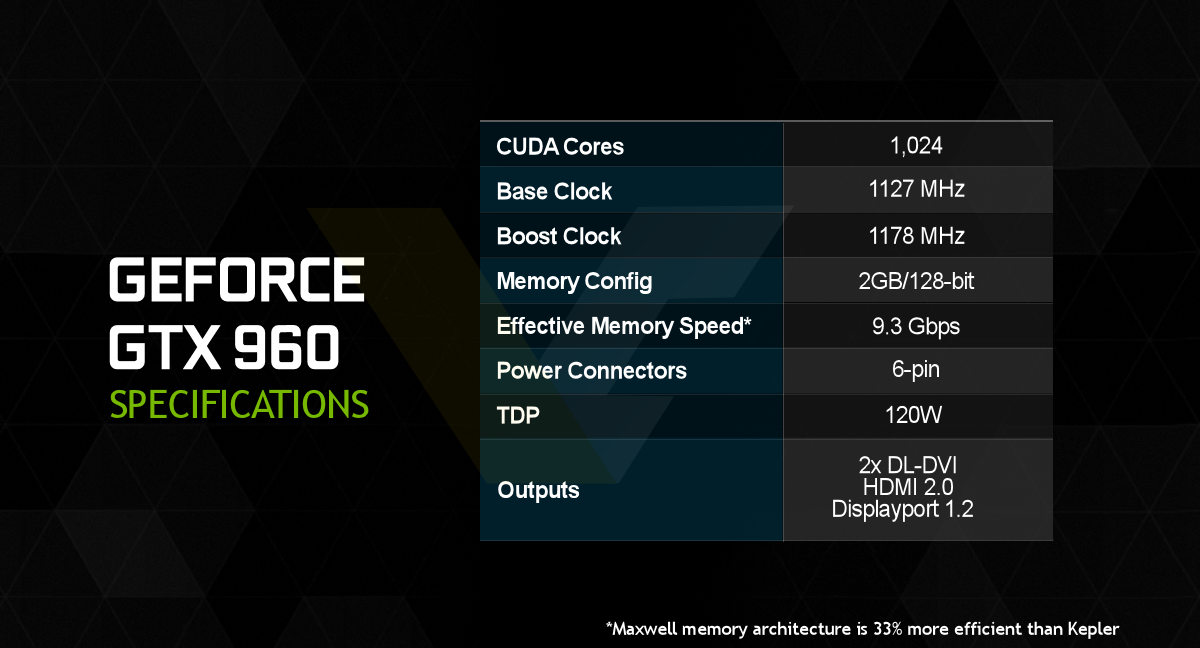
If newer hardware 16.04 would be generally be better. Consequently, we used a measurement probe to record the maximum temperature.Asus also often needs another boot parameter: pci=nomsi The actual hotspot is just next to what’s shown on the picture due to the card’s backplate. The updated and improved BIOS will be used for mass production of the card. We received the updated graphics card just in time, and decided to present both a “before” and “after” picture here. As we’ll see later, the problem could be solved to some degree by changing the fans’ response curve in the BIOS. We’ve contacted the manufacturer’s headquarters to find a solution for this before the launch. At a normal gaming load in a closed case, the card reaches 110 degrees Celsius, which is way too high. This is great for the noise level, but bad for the voltage converters, which are left to fend for themselves. After all, what good does a huge cooler do if the power converters only get a small aluminum strip? Ironically, the powerful GPU cooler makes things worse, since it cools the GPU so well that it only needs to spin its fans very slowly. This graphics card sports the exact opposite of the perfect cooling solution of the two Gigabyte graphics cards. Underneath the backplate, the VRM pins reach up to 95 degrees Celsius. It turns out that the actual temperatures stay hidden this way. Unfortunately, the few graphics card samples available in Germany have to be passed from reviewer to reviewer, so taking off the backplate isn’t allowed. Our temperature measurements show almost 79 degrees Celsius on the top of the board, which prompted us to insert a temperature sensor between the board and the backplate. This is counterproductive from a cooling point of view, so its presence is quite simply due to looks. Asus GTX 960 Strixįor no obvious reason, this very short graphics card has a completely closed backplate. This is why we use an Optris PI450, which doesn’t just provide us with high-definition pictures in real time, but also allows us to exactly define all measurement points. The largest measurement errors tend to occur when using normal infrared thermometers, which invariably have a dihedral angle that’s way too large to successfully measure the VRM pins and when the emissivity can’t be set exactly or is unknown.
The transparent lacquer, which is used by board manufacturers for the so-called tropicalization, is perfectly suited to the temperature measurement of the backs of boards and other surfaces which don’t have a known emissivity. We use either special tape or lacquer with known emissivity. Nothing’s worse than exact, but wrong, results. We’d like to point to our foundations article on temperature measurements here.
HOW TO GET NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 960M DRIVER FULL
If manufacturers take full advantage of this, then the load for every single power converter actually stays the same. The GPUs of this new generation produce much less waste heat, which makes them a lot easier to cool. The top picture shows an inexpensive, but bad solution. The following picture shows two different approaches to cooling the power converters. The temperature ranges we’re reporting are the minimums and maximums for the different builds under different loads (e.g., gaming, torture). With enough usage, these components might get damaged or become less reliable. Over time, the heat spreads across the board and to the passive and active components close to the voltage converters. If they hit temperatures around 100 degrees Celsius, they have a negative impact on the entire board. As usual, the voltage converters are the graphics cards’ problem area.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
